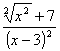Prérequis:
|
Voir : calcul de la
valeur numérique d’une
expression algébrique. |
|
|
Les nombres
relatifs |
|
|
CALCUL
NUMERIQUE |
ENVIRONNEMENT du
dossier:
|
Tableau |
DOSSIER: Calculs :recherche de valeurs
|
|
|
|
|
CORRIGE
|
|
A )On donne l’équation
y = 3,5 x ; calculer :
|
si x = 2 |
alors y = 7 |
|
si x = -2 |
alors y = -7 |
|
si x = 3/7 |
alors y =10,5 /7 ; = 1,5 |
|
si x = 5 |
alors y = 17,5 |
|
si x = - 3/4 |
alors y = 2,625 |
|
Si x = 2,75 |
Alors y = 9,625
|
B) On donne l’équation de la forme : y = a x ; calculer
:
|
si x = 4 |
et y = 67 +15 –
20 = |
alors a = 1,5 |
|
si x =-2,7 |
et y = 3,2 |
alors a = - 3,2
/2,7 ; -1,1851852 |
|
transformer l ’ égalité : si y = a x ;
alors a = (on dit :exprimer « a » en fonction de
« y » et « x » ; ou autrement dit : exprimer
« a » avec « y » et « x » ) |
C) trouver la valeur de « y » si l’on
donne une valeur à
«a ; x ; b » dans les cas suivants :
|
(remplir
le tableau suivant)Forme y = ax +b |
|
a = |
x = |
b = |
y = ax + b |
Résultat y = |
|
3 |
+2 |
+2 |
3 |
8 |
|
- 3 |
+2 |
+2 |
-3 |
-4 |
|
0,5 |
-2 |
+2 |
0,5 |
1 |
|
-1,5 |
-2 |
+3 |
-1,5 |
6 |
|
1 /
3 |
1 |
-0,5 |
1/3 |
-0,166666666 |
|
-
2 / 3 |
3 |
1,5 |
-(2/3) |
-0-5 |
D )Savoir résoudre les équations du premier :
SOS COURS
|
|
|
45 = 0,5 x |
x = 90 |
|
18 = |
x = 36 |
|
16= x + 0,5 |
x = 15,5 |
|
- 4,6 = 2,5 x + 1,3 |
x = -2,36 |
|
2,4 = |
x = -1,8 |
|
1,6 = -2 ,9 x |
x = - 0,551 |
Résoudre une équation du second degré à
une inconnue
|
I )
On considère les équations y1
= x2 ; y2
= 2x2 , y3
= -x2 et y4
= - 0,5x2.
|
x |
0 |
0,5 |
1 |
1,5 |
2 |
2,5 |
3 |
3,5 |
4 |
|
y1 |
0 |
0,25 |
1 |
2,25 |
4 |
6,25 |
9 |
12,25 |
16 |
|
y2 |
0 |
0,5 |
2 |
5,5 |
8 |
12,5 |
18 |
24,5 |
32 |
|
y3 |
0 |
-0,25 |
-1 |
-2,25 |
-4 |
-6,25 |
-9 |
-12,25 |
-16 |
|
y4 |
0 |
-0,125 |
-0,5 |
1,125 |
-2 |
-3,125 |
-4,5 |
-6,125 |
-8 |
II )
On considère les fonctions f1 = y1 ;
f2= y2 ;
f3= y3 et
y4 = f4, , telles que f1(x) = x2 f2(x) = 2x2 , f3(x)
= -x2 et f 4(x)
= - 0,5x2.
Compléter le tableau
suivant:
|
x |
0 |
0,2 |
0,5 |
0,8 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
f1(x) |
0 |
0,04 |
0,25 |
0,64 |
1 |
4 |
9 |
16 |
25 |
|
f2(x) |
0 |
0,08 |
0,5 |
1,28 |
2 |
8 |
18 |
32 |
50 |
|
f3(x) |
0 |
-0,04 |
-0,25 |
-0,64 |
-1 |
-4 |
-9 |
-16 |
-25 |
|
f 4(x) |
0 |
-0,02 |
-0,125 |
-0,32 |
-0,5 |
-2 |
-4,5 |
-8 |
-12,5 |
III )
On considère les fonctions f1
= y1 ; f2=
y2 ; f3= y3 et
y4 = f4, , telles que f1(x) = x2 f2(x) = 2x2 , f3(x)
= -x2 et f 4(x)
= - 0,5x2.
Compléter le tableau suivant:
|
x |
0 |
-0,2 |
-0,5 |
-0,8 |
-1 |
-2 |
-3 |
-4 |
-5 |
|
f1(x) |
0 |
0,04 |
0,25 |
0,64 |
1 |
4 |
9 |
16 |
25 |
|
f2(x) |
0 |
0,08 |
0,5 |
1,28 |
2 |
8 |
18 |
32 |
50 |
|
f3(x) |
0 |
-0,04 |
-0,25 |
-0,64 |
-1 |
-4 |
-9 |
-16 |
-25 |
|
f 4(x) |
0 |
-0,02 |
-0,125 |
-0,32 |
-0,5 |
-2 |
-4,5 |
-8 |
-12,5 |
Comparer
avec le tableau précédent et conclure.